Get Answers to Frequently Asked
Questions
Question and answer topics
About cystinuria
Q: What is cystinuria?
A: Cystinuria is a rare, lifelong disorder characterized by a lack of specific proteins
that help remove cystine from the urine. Without these proteins, cystine levels become too high, form into crystals, and grow into a specific type of kidney stone.
See how cystinuria affects your body in this video.
Q: What is cystine?
A: Cystine is an essential amino acid – a building block of protein – that is present
in humans. People with cystinuria have elevated levels of cystine in the urine that can build up to form crystals and grow into stones.
Q: How do people get cystinuria?
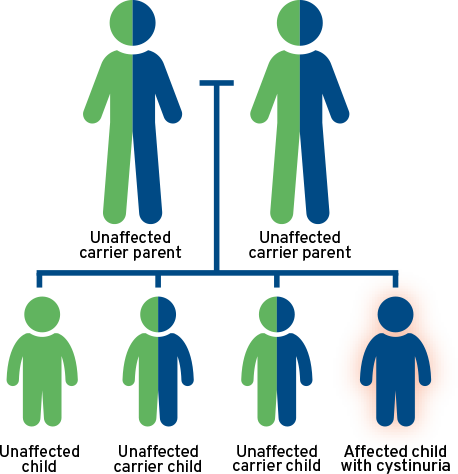
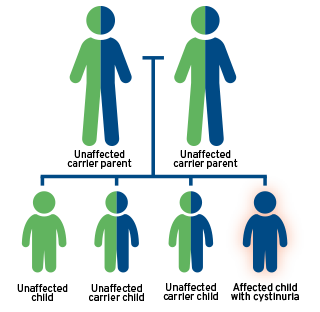
A: An autosomal recessive disorder, cystinuria is inherited only when both parents
are carriers of a specific rare gene and both pass it on. People are born with cystinuria when they inherit one abnormal gene from each parent.
Learn more about how you inherited cystinuria and your risks of passing it to your children.
Q: If a family member or my spouse has tested positive for cystinuria or is a carrier of the cystinuria gene, should I get tested?
A: Because cystinuria is inherited, you should consider a genetic test if a close
family member has the disease or is a carrier of the gene. If your spouse has a gene mutation that can cause cystinuria, you should get tested to determine if you also carry it, since two carrier parents may pass the gene to their children.
Q: What are the symptoms of cystinuria?
A: Cystinuria may be suspected if you form kidney stones at a young age, have
recurring kidney stones, experience flank pain, have a family history of kidney stones, or have cystine crystals in your urine.
Learn more about the early warning signs of cystine buildup by watching this video.
Q: Is cystinuria contagious?
A: Cystinuria is a genetic disease that is inherited. It is not contagious.
Q: Will my children inherit the gene mutation for cystinuria? If I become pregnant, can my unborn baby get it?
A: If both parents have this rare gene mutation and both have passed it to the embryo, the baby could develop cystinuria. For that reason, partners and siblings of people with cystinuria should consider genetic testing for cystinuria. Cystinuria is not a contagious disease and is not spread by infection. It cannot be "caught" by the unborn baby like an infection.
Q: Will cystinuria permanently damage my kidneys?
A: Up to 70% percent of patients experience kidney damage or long-term kidney
disease. Once damaged, kidneys do not improve; however, compliance with dietary modifications and medications can help prevent or minimize damage. Regular 24-hour urine tests to ensure that cystine levels stay below 250 mg/L – the point of solubility, above which stones are most likely to form – are extremely important. These test results help your doctor determine your risk and adjust your treatment plan to help prevent stone formation and kidney damage. A glomerular filtration rate (GFR) test can tell your doctor how well your kidneys are working.
Q: Is cystinuria curable?
A: There is currently no cure for this life-long disease. If untreated, people with cystinuria will likely continue to form cystine stones throughout their lifetimes. Cystinuria can, however, be managed with proper treatment and medication.
Testing for cystinuria
Q: How do I test for cystinuria?
A: Your doctor may ask you to perform an initial 24-hour urine collection test to
check the level of cystine in your urine. A microscopic examination of your urine sample will identify any cystine crystals. Follow-up 24-hour urine tests will be ordered periodically to ensure that cystine levels stay below the 250 mg/L solubility limit. Levels above this limit may permit kidney stone formation. Ultrasounds or low-dose CT scans may also be performed to determine if kidney stones are present in the body. If a stone is available, it should be analyzed for cystine content.
Watch this video to learn more about the 24-hour urine test.
Q: What is an eGFR test?
A: An estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) test is a blood test that measures how well your kidneys are filtering your blood. An eGFR of 60 or higher is normal, a result below 60 may indicate kidney disease, and a result of 15 or lower may indicate kidney failure.
Q: What other tests are important?
A: It is important to keep a close watch on your blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels, as high levels in these areas are risk factors for kidney disease or failure.
Treatment for cystinuria
Q: How much water do I need to drink?
A: Plenty of water is extremely important. Doctors recommend 4 liters – or about
4 quarts – of water a day, or enough to produce a minimum of 3 liters of urine per day. Increasing fluid intake helps to dilute cystine in the urine, making it harder for stones to form.
Q: What else can help manage my cystinuria?
A: Alkali supplements in the form of potassium citrate tablets are usually
recommended to make your urine less acidic and increase urine pH to a goal of 7.0 to 7.5.
Learn more about methods you can use together to manage cystinuria in the video above.
Q: What kind of diet is recommended for cystinuria patients?
A: Animal proteins should be limited to fewer than 8 ounces a day for adults,
and sodium intake should stay below 2300 mg, or 1 teaspoon, of salt a day. Because children need protein for growth, protein restrictions are not recommended for them.
Q: Will I need surgery if I have cystinuria?
A: Because cystine stones are typically larger and harder than other kidney
stones, surgery is sometimes required to remove them. However, maintaining a preventative treatment plan can often prevent new stones from forming. Surgical options include ureteroscopy (an outpatient procedure using a small scope inserted into the bladder and ureter) and, for larger stones, percutaneous nephrolithotomy, or PCNL (stones are removed using a scope inserted through a small incision in the back).
Q: Will I ever need to go to the ER? If so, when?
A: Seek immediate medical treatment if you experience any of these symptoms:
severe pain in the abdomen, groin, genitals, or side; blood in your urine; fever and chills or nausea and vomiting; or difficulty passing urine. If possible, choose an ER in the hospital with which your doctor has an affiliation. Also, if possible, consider calling your doctor before leaving for the ER. Your doctor may be able to call ahead and give the ER information about your condition.
THIOLA EC and generics
Q: Are generics available for THIOLA or THIOLA EC?
A: A generic is available for immediate release tiopronin. Brand name THIOLA and THIOLAEC are available only through the Total Care Hub.
Q: What can you do to ensure you receive brand name THIOLA and THIOLA EC?
A: Maintaining a treatment plan that works for you is important. If you would like to ensure you receive brand name THIOLA and THIOLA EC, there are a few things you can do:
1. Talk to your doctor about adding Dispense As Written (DAW) to your prescription form to ensure you receive brand name THIOLA or THIOLA EC
2. Check that the prescription and pill bottle label says THIOLA or THIOLA EC
3. Contact the HUB to confirm your brand name THIOLA or THIOLA EC prescription
Q: What if I have been prescribed generic tiopronin?
A: Notify your pharmacist and talk to you doctor immediately to request brand name THIOLA EC for all new prescriptions and refills moving forward. Call the Total Care HUB to alert them of the substitution.
THIOLA EC information
Q: What is THIOLA EC and how does it help?
A: In people with cystinuria, excess amounts of a substance called cystine accumulate in the urine. This can cause cystine stone formations.
THIOLA EC is a prescription medication for people with cystinuria. It is a thiol-binding medication that lowers the amount of excess cystine in the urine by binding to it, and turning it into a substance that is more easily dissolved in the urine.
Q: What is the difference between THIOLA and THIOLA EC?
A: THIOLA EC has the same active ingredient as THIOLA, but it comes in two tablet strengths, 100 mg and 300 mg. Because THIOLA is only available as a 100-mg tablet, THIOLA EC may allow you to take fewer pills per day. It also has an enteric coating, which allows it to be taken with or without food.
Q: How do I get THIOLA EC?
A: THIOLA EC is available only through the specialty pharmacy at the THIOLA EC
Total Care Hub®. After your doctor enrolls you, your medication will be conveniently mailed directly to you since it is not available at a traditional pharmacy.
THIOLA and THIOLA EC are available with no interruption in supply. The services and support provided by the THIOLA EC Total Care HUB® will continue to be available to those prescribed brand name THIOLA and THIOLA EC. Continue to get brand name THIOLA or THIOLA EC by asking your doctor to write Dispense As Written (DAW) on your prescription form.
Q: How can I ensure I am receiving brand name THIOLA or THIOLA EC?
A: 1. Talk to your doctor about adding Dispense As Written (DAW) to your prescription form to ensure you receive brand name THIOLA or THIOLA EC
2. Check that the prescription and pill bottle says THIOLA or THIOLA EC
3. Contact the HUB to confirm your brand name THIOLA or THIOLA EC prescription
Q: What is the usual dose of THIOLA EC?
A: The recommended starting dose for adults is 800 mg a day, divided into three
doses a day. In clinical studies, the average dosage was about 1000 mg/day. Your dose will be adjusted based on the amount of medication needed to reduce cystine levels in your urine below the solubility limit of 250 mg/L.
Q: Can children take THIOLA EC?
A: Yes, children who weigh at least 20 kg, or 44 lbs, can take THIOLA EC. The
recommended initial dose for children is based on body weight: 15 mg/kg/day. For example, the dose for a child weighing 44 lbs would be 300 mg/day. Avoid dosages greater than 50 mg/kg/day in pediatric patients. Note that THIOLA EC tablets must be swallowed whole and should not be crushed or broken.
Q: Can THIOLA EC tablets be broken or crushed?
A: No. Tablets must be swallowed whole.
Q: Why do I need to take THIOLA EC 3 times a day?
A: THIOLA EC works fast and is eliminated from the body quickly. If you skip a
dose, you increase your risk of forming stones.
Q: Do I need to take THIOLA EC with meals?
A: THIOLA EC may be taken with or without food. Because food affects how THIOLA EC is absorbed, your doctor may increase your dosage if you routinely take it at mealtimes. Take your THIOLA EC around the same times each day, and maintain a routine pattern regarding which doses you take with meals. Tablets must be swallowed whole.
Q: Why is my dose different with THIOLA EC?
A: Your doctor may have adjusted your individualized dose based on the
results of your 24-hour urine test.
Q: Can I drink alcohol while taking THIOLA EC?
A: Alcohol should be avoided 2 hours before and 3 hours after taking THIOLA EC.
Q: Are there any side effects with THIOLA EC?
A: Side effects vary. Talk to your doctor about what to expect and how to manage
any side effects should they occur. The most common side effects include nausea, diarrhea or soft stools, sores in the mouth, rash, fatigue, fever, muscle or joint pain, high amounts of protein in the urine, and vomiting.
Serious side effects include proteinuria (high amounts of protein in the urine), serious kidney problems, and hypersensitivity reaction (including fever, rash, joint pain, and enlarged or swollen lymph nodes).
Q: Can THIOLA EC be taken while pregnant?
A: Tiopronin is the active ingredient in THIOLA EC and there are no published
reports of tiopronin-associated risks for major birth defects, miscarriage, or maternal or fetal side effects. Renal stones in pregnancy may result in adverse pregnancy outcomes. Talk to your doctor about the potential risks and benefits of taking THIOLA EC during pregnancy.
Q: Can THIOLA EC be taken while breastfeeding?
A:Breastfeeding is not recommended while taking THIOLA EC.
Communicating with your healthcare team
Q: What doctors will I need to see for cystinuria?
A: Urologists treat cystinuria and can perform surgery to remove stones.
Nephrologists specialize in kidney diseases.
Q: What information should I share with my doctor?
A: It is important to build a relationship with your doctors. Tell them about any
stones passed, stone-related pain, visits to the ER, and difficulties following your treatment plan.
Patient support programs
Q: What is the THIOLA EC Total Care Hub?
A: The Total Care HUB, administered by Specialty Pharmacy, EVERSANA, is the ONLY dispensing pharmacy for brand name THIOLA and THIOLA EC.
Services available on the Total Care Hub include prescription refills and
delivery; patient assistance programs for the uninsured; reimbursement help; and live information and support from Hub counselors, pharmacists, and nurses.
Q: What is myHUB?
A: A part of the THIOLA EC Total Care Hub, myHUB offers live events and
personalized support through texts, emails, or phone calls for patients managing their cystinuria. You can register for myHUB here.
Q: Do I need a prescription for THIOLA EC to get information about managing cystinuria?
A: No, you can register for myHUB without a prescription through this link. Once
you do, you will receive information about cystinuria and how to manage it.
